Central Bank Raises 2025 Inflation Forecast

The Central Bank raised the year-end 2025 inflation forecast from 21% to 24%. Inflation predictions for 2026 and 2027 were set at 12% and 8%, respectively. The TCMB President, Karahan, stated that this revision does not signal any relaxation. Addressing the interest rate cut cycle, Karahan said, “We are not on autopilot, we are data-driven.”
The Central Bank (TCMB) President Fatih Karahan presented the first inflation report of the year at the Istanbul Finance Center. The TCMB raised the 2025 inflation forecast from 21% to 24%, while it was set at 12% for 2026 and 8% for 2027.
Karahan emphasized that this revision does not signal relaxation, stating, “We will maintain our tight stance in monetary policy until a sustainable decrease in inflation and price stability is achieved.”
When asked about further interest rate cuts, Karahan replied, “We are not on autopilot, we are data-driven. We believe that we have a certain range, and we will act prudently.”
“DEFLATIONARY PROCESS CONTINUES”
Highlights from Karahan’s remarks:
Our deflationary process continues, and macroeconomic indicators are progressing in line with this process.
Recently, we have observed a substantial increase in the uncertainty of global trade policies.
Market pricing in both developed and developing countries indicates that interest rates will be cut more slowly in 2025.
“STABLE TRENDS IN DOMESTIC DEMAND WILL CONTINUE”
Current industrial production indicators for the fourth quarter point to a moderate recovery in economic activity.
Overall, data related to demand conditions suggests that demand is at supportive levels for a decline in inflation. I would like to emphasize that, due to our tight monetary policy, a balanced trend in domestic demand will persist. The output gap will continue to be a significant component in the deflation process, staying in the negative zone in the near term.
“INCREASE EXPECTED IN TRADE DEFICIT”
We expect an increase in the trade deficit in the upcoming period. However, this increase will be limited due to our tight monetary stance. We anticipate that the trade deficit in 2025 will continue to be below the historical average as a share of national income.
The main downward trend in inflation continued in the last quarter. However, the core trend increased in January as projected.
In January, there was a higher price rise in the time-dependent pricing group. On the other hand, items with flexible pricing mechanisms showed lower price increase rates compared to the previous year.
IMPACT OF CO-PAYMENT ON INFLATION
Following the first increase in official health check-up co-payments since 2017, there was a 0.6-point impact on January’s consumer inflation. Moreover, the effects of this adjustment will carry over to February’s inflation.
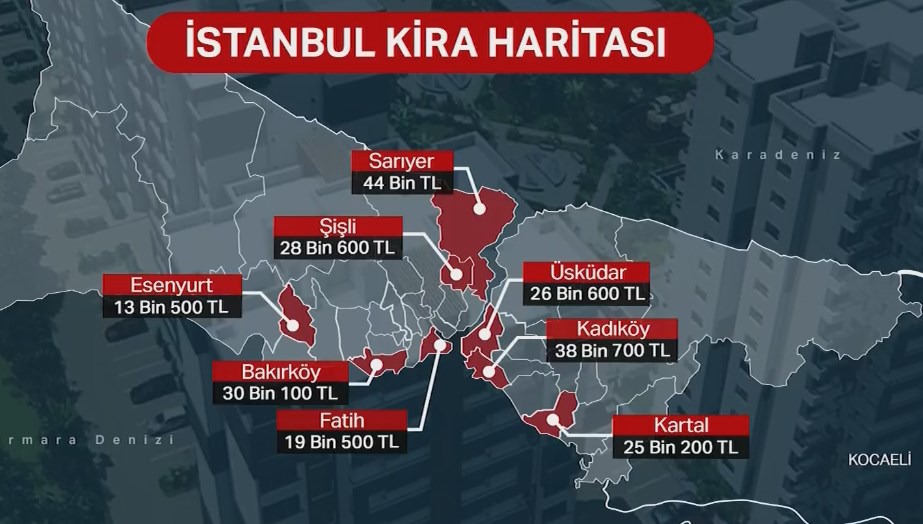
RENT INFLATION SLOWING DOWN
Although rental inflation remains high, it is showing signs of slowing down. The monthly increase in rental inflation in January was due to a rise in the rate of rental contract renewals.
We can say that the pressure from producer prices on consumer inflation, especially in basic goods, is moderate.
Recent declines in consumer and business inflation expectations have become more pronounced. With our determined stance in monetary policy, this improvement in expectations will continue.
“DEPOSIT INTEREST SUPPORTS TRANSITION TO TURKISH LIRA”
We support the effectiveness of monetary transmission through macro-prudential measures and liquidity management.
We sterilize the excess liquidity in the market using mandatory reserves and our existing tools.
Thanks to our monetary policy stance and macro-prudential framework, the level of deposit interest rates continues to support the transition to the Turkish lira and savings.
“END IN SIGHT FOR RESERVE OPTION MECHANISM”
Considering the current level of the Reserve Option Mechanism (ROM), we plan to conclude this practice during the year favoring legal entities.
The increasing confidence of domestic and foreign residents in the Turkish lira continues to have a positive impact on our reserves.
INFLATION FORECAST RAISED
Inflation is estimated at 24% for 2025, 12% for 2026, and 8% for 2027.
After the inflation decreases to 8% in 2027, we aim for it to stabilize at 5% in the medium term. The update in the 2025 forecast was driven by factors beyond the relative impact area of monetary policy.
This revision stems from factors outside the relative impact area of monetary policy, thus not signaling any relaxation in the monetary policy stance.